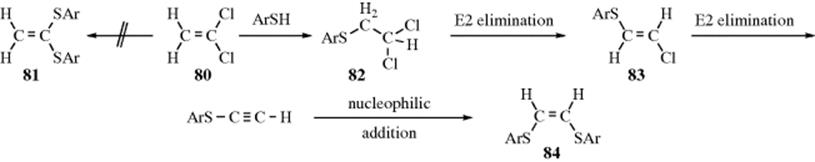
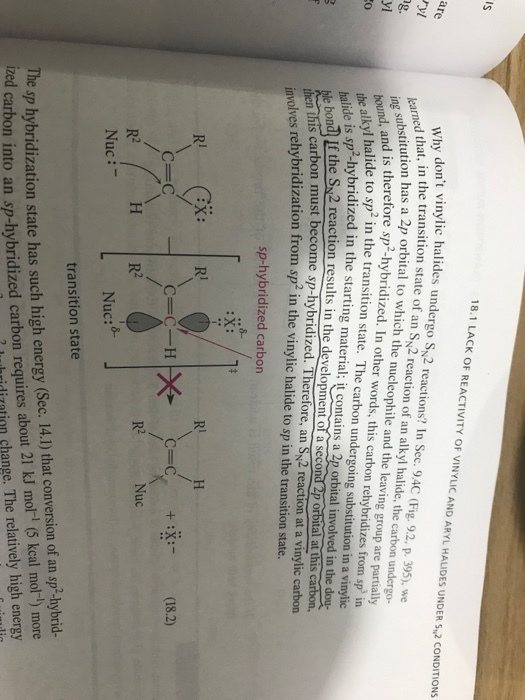
Nucleophilic substitution at a vinylic carbon is difficult under normal condition and is extremely slow compared to substitution at saturated carbon.
Substitution at vinylic carbon.
This explains the product distribution or.
1989 54 5 998 1000.
Nucleophilic substitution at unactivated vinylic carbon.
In 1935 edward d.
The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon.
The two main mechanisms are the s n 1 reaction and the s n 2 reaction.
The most common mechanisms are the tetrahedral mechanism and the closely related addition elimination mechanism.
1 for such a concerted bimolecular nucleophilic substitution at a vinylic sp 2 carbon are proposed two possible mechanisms namely in plane.
Both of these mechanisms are impossible at a saturated substrate.
S stands for chemical substitution n stands for nucleophilic and the number represents.
Nucleophilic substitution at a vinylic carbon 252 is difficult see sec.
Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule.
The vinyl chloride are essentially inert towards nucleophiles.
Journal of the american chemical society 2000 122 10 2294 2299.
It is encountered in nucleophilic substitution.
10 g i but many examples are known.
S n2 s n2 is a type of reaction mechanism that is common in organic chemistry.
Concerted nucleophilic substitution at an sp 3 carbon typically bimolecular nucleophilic substitution s n 2 reaction is one of the most fundamental reactions in organic chemistry giving a substitution product with inversion of the configuration.
Vinyl c x bond x halogen oxygen nitogen is stronger than the alkyl c x bond because of a resonance interaction.
Introduction the addition elimination route is the most studied one in scheme 1.
In reaction conditions that favor a s n 1 reaction mechanism the intermediate is a carbocation for which several resonance structures are possible.
An allylic rearrangement or allylic shift is an organic reaction in which the double bond in an allyl chemical compound shifts to the next carbon atom.
Hughes and sir christopher ingold studied nucleophilic substitution reactions of alkyl halides and related compounds.
They proposed that there were two main mechanisms at work both of them competing with each other.
Factors conducive to the energetic preference for the in plane sn2 pathway.
Since it involves a reaction of the nucleophile with the vinylic carbon atom it is also the one which in actual fact is most correctly described as a nucleophilic vinylic substitution.